Keeping freshwater sharks in aquariums is a very enjoyable yet challenging experience. To keep these fish healthy, it is essential to provide them with the right environment and care. Moreover, not all freshwater sharks are suitable for aquariums.
I have been working extensively and gaining experience with freshwater sharks for aquariums for many years. I am currently raising some freshwater sharks that are suitable for keeping in my aquarium.
Here, I am discussing all the sharks I keep in my aquarium in light of my experience.
Golden Shark
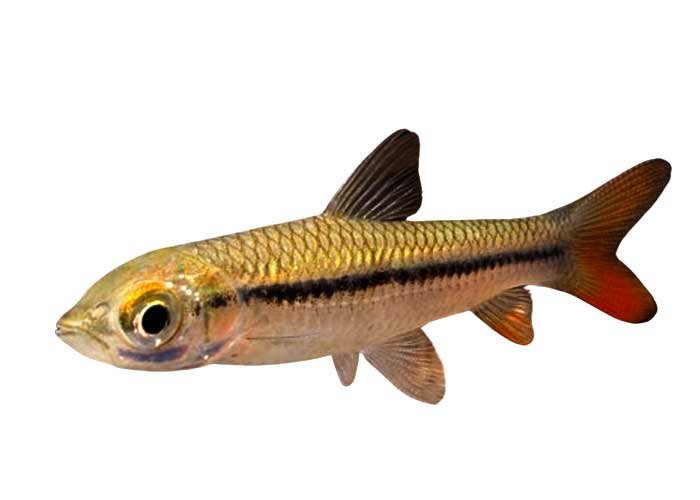

Golden-Shark
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Epalzeorhynchos frenatum
- Common Names: Golden Shark, Rainbow Shark, Red-Finned Shark
- Family: Cyprinidae (Carp family)
- Size: Typically grows up to 6 inches (15 cm) in captivity
- Behavior: Semi-aggressive; territorial, especially toward other bottom-dwellers and similar-looking fish
- Origin: Native to Southeast Asia, primarily in rivers and streams in Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam
- Lifespan: 5-8 years in captivity with proper care
Residence
- Minimum Tank Size: 50-55 gallons (around 189 to 208 liters). The tank should be at least 4 feet in length for swimming and territorial separation.
- Plants: Suitable plants for Golden Sharks are Anubias, Java Fern, Amazon Sword, or Hornwort, as these plants create an environment that mimics their natural habitat and provide safety and hiding places for the fish.
- Decor: Include plenty of hiding places, such as rocks and caves, to reduce aggression and provide hiding spots.
Care of Golden Shark
Water Conditions and Parameters: The ideal temperature for them is 22-27°C (75-80°F). Ideal pH: 6.0 to 8.0. The ideal water hardness is 5 to 11 dGH. Ammonia and nitrate levels should be zero.
Water Changes: Change 20-25% of the water every week to maintain water quality.
Food Habits: Primarily omnivorous, they eat a variety of foods, such as:
- Natural Foods: Small aquatic plants, algae, small insects, and mollusks found in the substrate
- Flake and Pellet Food, Vegetables: Pumpkin, cucumber, spinach, etc.Protein-Rich Foods: Bloodworms, brine shrimp, daphnia, etc., along with algae, which also helps keep their aquarium clean.
Breeding: Golden Sharks are difficult to breed in an aquarium due to their specific environmental and behavioral needs. They require controlled water parameters, temperature, specific tank setups, and often hormone treatments for successful breeding. In commercial settings, Golden Sharks are bred.
Suitable Tank Mates
Due to their semi-aggressive, territorial nature, suitable tank mates should be peaceful, such as loaches, danios, gouramis, and rainbowfish.
Cosmic-Blue-Glo-Shark

Cosmic-Blue-Glo-Shark
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Epalzeorhynchos frenatum (for GloFish shark, genetically modified from the Rainbow Shark)
- Common Name: GloFish Shark, Rainbow Shark
- Family: Cyprinidae (Carp family)
- Size: Around 4-6 inches (10-15 cm)
- Behavior: Semi-aggressive, especially in smaller tanks.
- Origin: Artificially bred, originally from Thailand, Cambodia, Laos (native to the Rainbow Shark)
- Lifespan: Approximately 5-8 years in captivity with proper care
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: A Cosmic Blue Glo Shark requires a tank of at least 50-60 gallons (189 to 227 liters). Because these fish are very active, it is important for them to have enough space.
If the tank is large and has lots of hiding places, it is advantageous for the fish.
Plants: Suitable plants for the Cosmic-Blue-Glo-Shark are Anubias, Java fern, Amazon sword, hornwort, and Marimo ball because these plants mimic their natural habitat and provide security and hiding places for the fish.
Care of Cosmic-Blue-Glo-Shark
Water Conditions and Parameters: The ideal temperature for them is 23-27°C (74-80°F). Ideal pH: 6.5 to 7.5. The ideal water hardness is 5 to 12 dGH. Nitrate: Below 20 ppm. Ammonia and nitrite levels are zero.
25-30% of the water should be changed every week to maintain water quality.
Food Habits: They are usually among the different species of golden sharks, so they are basically omnivorous. Like the golden shark, they enjoy eating a variety of foods such as:
- Natural foods (small aquatic plants, algae, small insects, and mollusks found in the soil)
- Flake and pellet foods
- Vegetables (pumpkin, cucumber, spinach, etc.)
- Protein-rich foods (bloodworms, brine shrimp, daphnia, etc.)
Breeding
They are usually a subspecies of the golden shark, so they are difficult to breed in an aquarium due to their specific environmental and behavioral requirements, like the golden shark.
They require controlled water parameters, temperature, specific tank setups, and often the use of hormone treatments.
Suitable Tank Mates
Since it is semi-aggressive, it can be a bit aggressive at times, especially if there are other fish in their swimming area. Suitable tank mates for them can include Tetras, Zebra Danios, Corydoras Catfish, Guppies and Mollies, and Plecos.
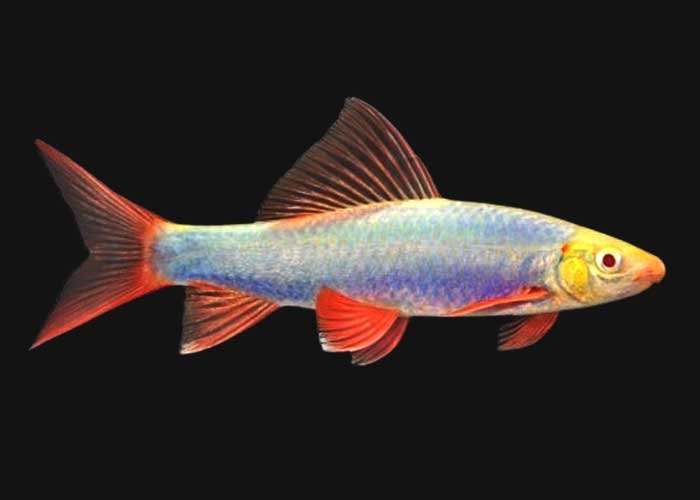
Red Tail Shark
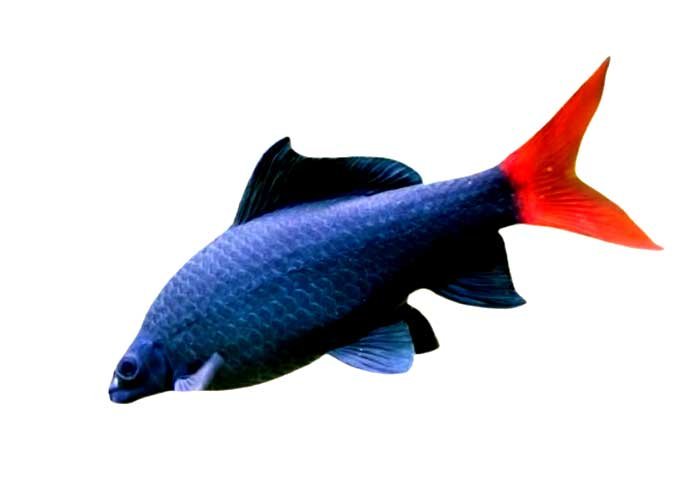
Red Tail Shark
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Epalzeorhynchos bicolor
- Common Name: Red Tail Shark, Red Tail Black Shark.
- Family: Cyprinidae
- Size: Up to 6 inches (15 cm) in length.
- Behavior: Semi-aggressive and territorial, especially toward its own species and similar-looking fish; best kept alone or with compatible tank mates.
- Origin: Native to freshwater streams in Thailand; now mostly bred in captivity due to being endangered in the wild
- Lifespan: Typically 5 to 8 years in captivity with proper care.
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: 50-55 gallons (around 189 to 208 liters). The tank should be at least 4 feet in length for swimming and territorial separation.
Plants: Some special types of plants can be kept in the Red Tail Shark fish tank, which are helpful in creating a healthy and suitable environment for them. Some plants that are good for the Red Tail Shark: Java Fern, Anubias, Amazon Sword, Cryptocoryne, and Java Moss.
Care of Red Tail Shark
Water conditions and parameters: The Red Tail Shark is a popular freshwater fish that requires specific water conditions to thrive. Here are the key water parameters for the Red Tail Shark:
- Water Temperature: 22°C to 26°C (72°F to 80°F)
- pH Level: 6.5 to 7.5
- Water Hardness: 4 to 12 dGH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm (parts per million)
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
- Nitrate: Below 20-40 ppm
Note: 25-30% of the water should be changed every week to maintain water quality.
Food Habits:
The Red Tail Shark is an omnivorous fish that can eat almost anything it catches.
- Plant foods: They can eat plant foods such as algae, aquatic plants, and vegetables (blanched spinach, lettuce, and spirulina).
- Animal foods: They can also eat animal foods such as worms, insect larvae, and small invertebrates like small fish in their natural habitat.
- Commercial fish foods: They can also eat high-quality pellets and flakes.
Breeding
The reproduction process of the Red Tail Shark occurs in the natural environment where they can spawn (lay eggs). However, their reproduction is less common in aquarium environments. This is probably due to the lack of their natural environment or lack of nutrients.
Suitable Tank Mates
The Red Tail Shark is a semi-aggressive fish that prefers to be kept alone. However, there are some fish that do not have any problems keeping the Red Tail Shark with them, such as Danios, Tetras, Corydoras Catfish, Rainbowfish, and Loaches.
Flying-fox-shark

Flying-fox-shark
Species Overview
• Scientific Name: Epalzeorhynchos kalopterus
• Common Name: Flying Fox Shark, False Siamese Algae Eater
• Family: Cyprinidae
• Size: Typically grows up to 5-6 inches (12-15 cm) in captivity
• Behavior: Semi-aggressive, territorial; can be aggressive toward similar species or bottom dwellers; known for algae-eating habits
• Origin: Southeast Asia, primarily found in Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia
• Lifespan: Typically 8-10 years in a well-maintained aquarium
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: A tank size of at least 40 gallons (about 150 liters) should be suitable for the Flying Fox Shark. This fish can grow to about 6 inches (15 cm) and is a very active swimmer, so adequate swimming space is important.
Plants: Flying Fox Sharks are quite active, so it is very important to choose suitable plants for them in the aquarium, as these plants provide them with safe shelter, shade, and a natural environment. Some suitable plants for Flying Fox Sharks are Java Fern, Anubias, Amazon Sword, Java Moss, and Vallisneria.
Care of Flying Fox Shark
Water Conditions and Parameters: Flying Fox Sharks require proper water quality and environment to be healthy and happy. The ideal water conditions and parameters for them are:
• Water Temperature: 23°-27°C (71°-81°F)
• pH Level: Typically 6.5 to 7.5
• Water Hardness: 5 to 15 dGH
• Ammonia: 0 ppm (parts per million)
• Nitrite: 0 ppm
Note: 25-30% of the water should be changed weekly to maintain proper water quality and remove waste.
Food Habits: Flying Fox Sharks are omnivorous fish. They can naturally eat algae, frozen or live foods (brine shrimp, daphnia, and bloodworms), flake food, pellets, and vegetable-based foods (cooked spinach, cucumber, zucchini, etc.).
Suitable Tank Mates
The Flying Fox Shark is a semi-aggressive and active fish, often territorial. It requires the right tank mates to be selected. Some suitable tank mates are Danios, Tetras, Rainbowfish, Corydoras Catfish, Plecos, and Loaches.
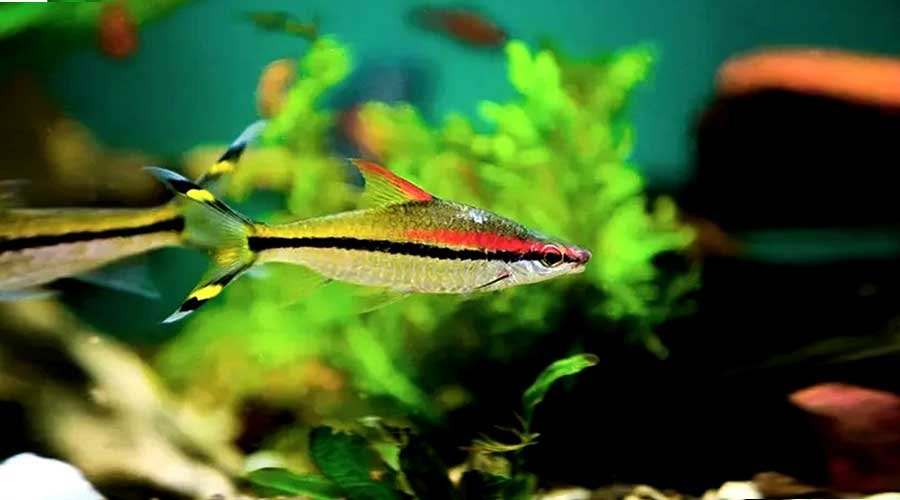
Roseline-Sharks
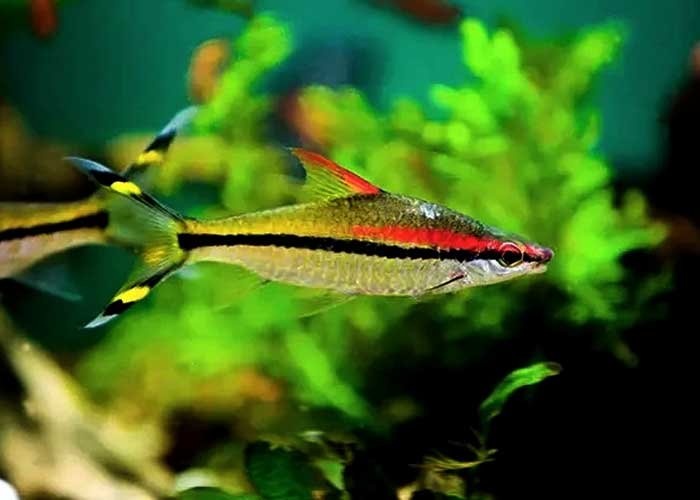

Roseline-Sharks
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Sahyadria denisonii
- Common Name: Roseline Shark, Denison’s Barb, Red-Line Torpedo Barb
- Family: Cyprinidae (the carp family)
- Size: Adult Roseline Sharks typically grow to about 6 to 7 inches (15 to 18 cm) in length.
- Behavior: These are peaceful fish that can coexist well with other non-aggressive fish species.
- Origin: The Roseline Shark is native to the rivers of India.
- Lifespan: In an aquarium, Roseline Sharks typically live 5 to 7 years.
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: The minimum tank size for Roseline Sharks is usually 50 to 60 gallons (190-227 liters) because these fish are active.
Plants: Roseline Sharks are usually fast-moving, so it is important to choose plants that will not hinder their movement and will provide them with nutrients. Some suitable plants for them are Java Fern, Anubias, Amazon Sword, Cryptocoryne, and Hornwort.
Care of Roseline-Sharks
Water Conditions and Parameters:
- Water Temperature: 18°-26°C (65°-79°F)
- pH Level: Typically 6.8 to 7.8
- Water Hardness: 5 to 25 dGH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm (parts per million)
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
Note: 25-30% of the water should be changed every week to maintain water quality.
Food Habits: These fish are generally omnivorous. They eat a mixture of protein and plant-based foods, including high-quality flake foods, frozen or live foods (such as brine shrimp, daphnia, and bloodworms), and even some vegetable matter such as algae-based tablets and blanched vegetables (spinach, zucchini, etc.).
Suitable Tank Mates
Roseline Sharks are peaceful and active fish. They can be kept with other similarly peaceful tank mates such as Tetras, Corydoras Catfish, Rainbowfish, Guppies, Mollies, Cherry Shrimp, etc.
Silver-Apollo-Shark
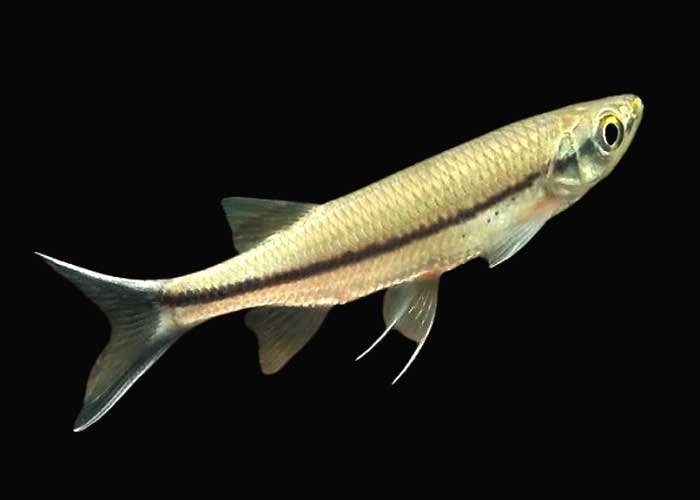

Silver-Apollo-Shark
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Luciosoma setigerum
- Common Name: Silver Apollo Shark, Apollo Shark, Long-Finned Barb
- Family: Cyprinidae (the carp and minnow family)
- Size: Typically grows up to 15–25 cm (6–10 inches) in length, though it can reach up to 30 cm (12 inches) in the wild.
- Behavior: This species is active and semi-aggressive, especially in small spaces.
- Origin: Native to Southeast Asia, particularly found in rivers and streams in Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia.
- Lifespan: Typically 5–8 years in captivity with proper care and conditions.
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: Silver Apollo Sharks are fast-swimming, active freshwater fish. To ensure a comfortable and healthy environment for them, a minimum tank size of 75 gallons (about 280 liters) is required.
Plants: Silver Apollo Sharks are fast-swimming, active freshwater fish. Suitable plants for their aquariums include Snake Plant, Peace Lily, and Money Plant.
Care of Silver-Apollo-Shark
Water Conditions and Parameters:
- Water Temperature: 20°-26°C (68°-79°F)
- pH Level: Typically 6.8 to 7.8
- Water Hardness: 5 to 20 dGH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm (parts per million)
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
Food Habits: Apollo Sharks are generally omnivorous fish, naturally eating a variety of foods. For example:
- Insects: Small fish or aquatic insects, such as larvae or worms.
- Algae: Also eats small amounts of algae and other plant matter.
- Flake Food and Pellets: Quality flake food or pellets made for aquariums are good foods for Apollo Sharks.
- Frozen Food: They also like to eat frozen foods such as bloodworms or brine shrimp.
- Vegetables: Occasionally, cucumbers, carrots, or small-boiled vegetables are also good foods for them.
Suitable Tank Mates
Silver Apollo Sharks are generally active and semi-aggressive, especially in small spaces. Therefore, they should be kept with certain fish to maintain a balanced tank environment. Suitable fish for them are Angelfish, Tetra fish (Neon Tetra, Cardinal Tetra), Gourami fish, Corydoras Catfish, and Pleco fish.
Chinese Algae Eater
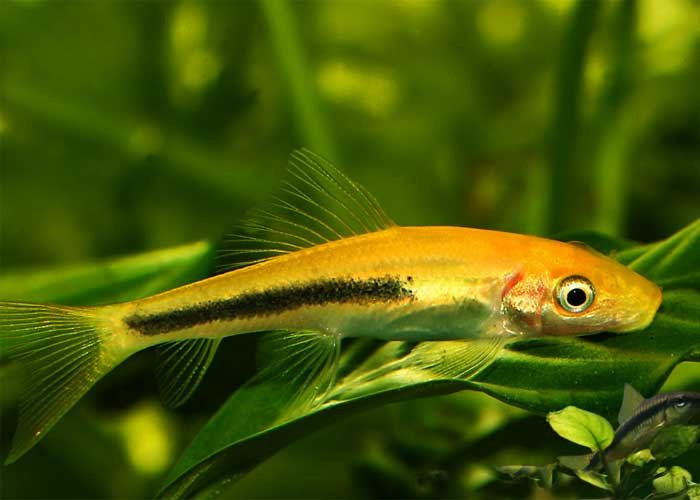

Chinese-Algae-Eater
Species Overview
• Scientific Name: Gyrinocheilus aymonieri
• Common Name: Chinese Algae Eater, SAE (Siamese Algae Eater), or Aymonier’s Algae Eater
• Family: Gyrinocheilidae
• Size: Typically grows up to 6-7 inches (15-18 cm) in length.
• Behavior: Chinese Algae Eaters are generally peaceful but can sometimes be territorial, especially as they grow.
• Origin: Native to Southeast Asia, specifically found in the rivers and streams of China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.
• Lifespan: In an aquarium setting, they typically live around 10 years, though this can vary based on water conditions and care.
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: Chinese Algae Eaters are generally peaceful but can sometimes be territorial, especially when large. Therefore, to ensure a comfortable and healthy environment for them, a minimum tank size of 50 gallons (about 189 liters) is required.
Plants: Chinese Algae Eaters can be a bit aggressive toward plants and other fish as they grow. Therefore, strong and fast-growing plants should be chosen, which can withstand the attacks of this fish. Suitable plants for them include Java Fern, Anubias, Amazon Sword, Java Moss, Hornwort, etc.
Care of Chinese Algae Eater
Water Conditions and Parameters: Chinese Algae Eaters are freshwater fish that require stable and suitable water conditions for optimal health. The recommended water parameters and conditions for them are:
- Temperature: 24-28°C (75-82°F)
- pH: 6.5-7.5
- Hardness: 5-20 dGH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm (toxic to fish)
- Nitrite: 0 ppm (also toxic)
- Nitrate: <20 ppm
Food Habits: There are several food options that are suitable for Chinese Algae Eater fish, which are helpful for their health and growth.
- Algae: Naturally occurring algae in the tank are ideal food for them. They eat algae from the glass, rocks, and other surfaces of the tank.
- Vegetables: They like to eat boiled cucumbers, spinach, pumpkin, and zucchini. They will eat vegetables if they are placed in the tank in small pieces.
- Protein-rich foods: Occasionally, a little protein-rich food such as bloodworms or brine shrimp should be added to their diet. However, such foods should be given in small quantities.
- Flake food and pellets: Flake or pellet food intended for other fish is also sometimes given to them.
Suitable Partners
The Chinese Algae Eater is a peaceful and herbivorous fish, but it can get along well with some fish and can also bother some companion fish. Their companions can include Tetras, Corydoras Catfish, Guppies, Mollies, Platies, Rainbowfish, etc.
Harlequin Sharks
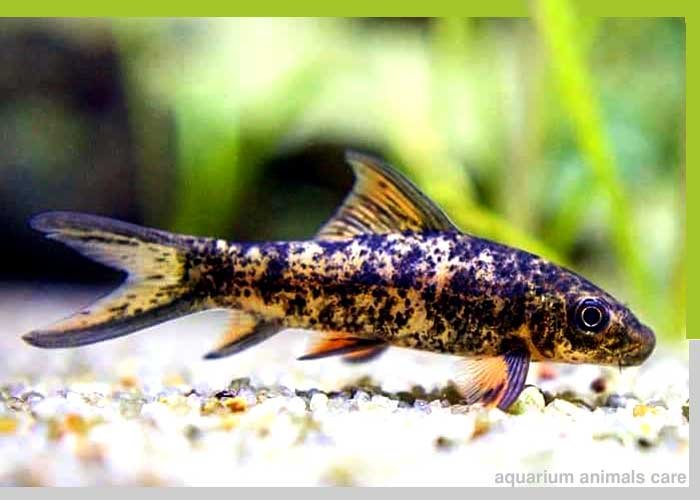

Harlequin-Sharks
Species Overview
- Scientific Name: Labeo cyclorhynchus
- Common Name: Harlequin Tusk Fish, Harlequin Shark
- Family: Labridae (Wrasse Family)
- Size: Typically reaches about 12 to 14 inches (30 to 35 cm) in length.
- Behavior: Harlequin tusk fish are semi-aggressive and territorial, especially when kept in confined spaces. They are known for their powerful jaws and sharp teeth.
- Origin: Found in the Indo-Pacific region, including areas around the Great Barrier Reef, Fiji, the Philippines, and Indonesia.
- Lifespan: They can live for about 10 to 15 years in an aquarium if properly cared for.
Residence
- Minimum Tank Size: Harlequin Sharks are fast-moving and prefer to be kept with multiple fish. Adequate tank size is very important for Harlequin Sharks, as they need space to grow and behave normally. A tank should be at least 55 gallons (208 liters) in size.
- Plants: Harlequin Sharks are strong and active fish, and sometimes they can damage plants. When choosing plants for them, select plants that grow quickly and can survive in harsh environments. Suitable plants for them include Anubias, Java Fern, Cryptocoryne, Amazon Sword, Hornwort, Java Moss, etc.
Care of Harlequin Sharks
Water Conditions and Parameters: Harlequin sharks are freshwater fish that thrive in specific water conditions. The ideal water parameters for them are:
- Water temperature: 22°C to 26°C (72°F to 79°F)
- pH Ideal range: 6.5 to 7.5
- Ideal Hardness range: 5 to 15 dGH
- Ammonia: 0 ppm
- Nitrite: 0 ppm
- Nitrate: <40 ppm
Food Habits: Harlequin Sharks prefer to eat mainly bottom food. However, they will also eat other foods.
- Sinking Pellets or Tablets: They can easily eat anything that sinks to the bottom.
- Algae Wafers: They love algae, so algae wafers can be a good food for them.
- Loose Vegetables: They will eat easily if you put sliced cucumber, spinach, or zucchini in small pieces in the aquarium.
- Brine Shrimp and Bloodworms: Frozen or live brine shrimp and bloodworms are very nutritious for them.
- Aquatic Plants: Harlequin Sharks will sometimes eat small aquatic plants. However, this should be kept to a minimum.
Suitable Partners
There are a few things to keep in mind when choosing aquarium companions for Harlequin Sharks, as they can be a bit aggressive by nature, especially regarding their territory. These fish are generally best kept with fish such as Tinfoil Barbs, Silver Dollar Fish, Plecostomus (Pleco), Giant Danios, and Bala Shark, as these fish do not claim their own territory.
Siamese-Algae-Eater
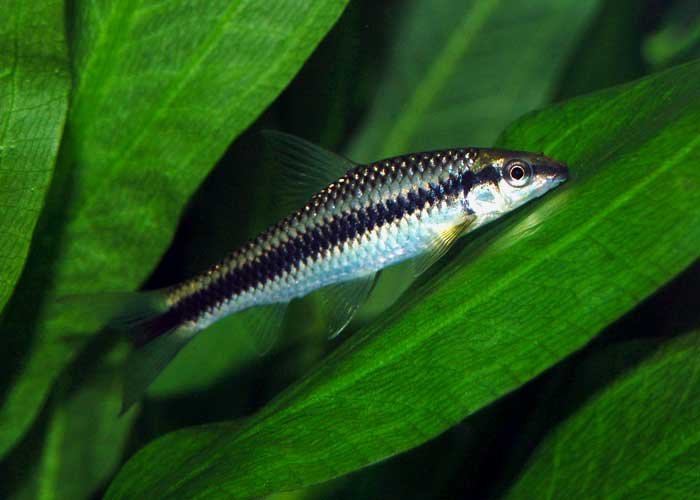

Siamese-Algae-Eater
Species Overview
• Scientific Name: Crossocheilus oblongus
• Common Name: Siamese Algae Eater (often abbreviated as SAE)
• Family: Cyprinidae
• Size: Typically 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm)
• Behavior: Peaceful and active, they can be easily kept with other peaceful fish.
• Origin: Native to Southeast Asia, specifically found in Thailand, Laos, and Cambodia.
• Lifespan: Around 10 years in captivity, with good care and appropriate tank conditions.
Residence
Minimum Tank Size: The minimum tank size for Siamese Algae Eaters is 40 gallons or about 150 liters. However, larger tanks are better for them, as they are quite active and prefer to stay in groups.
Plants: Siamese Algae Eaters primarily eat algae. Therefore, it is better to keep plants like Java Fern, Anubias, Amazon Sword, Java Moss, and Vallisneria in the aquarium, as they are compatible with these fish and provide a comfortable environment.
Care of Siamese Algae Eater
Water Conditions and Parameters: The Siamese Algae Eater is a popular aquarium fish. The ideal water conditions and parameters for them are:
• Water temperature: 24°C to 26°C (75°F to 79°F)
• pH level: 6.5 to 7.5
• Water hardness (GH): 5-20 dGH
• Ammonia: 0 ppm
• Nitrite: 0 ppm
Food Habits: The Siamese Algae Eater helps control algae in the aquarium by eating it. They can also eat a variety of other foods along with algae, such as:
• Vegetables: They like spinach, cucumber, zucchini, and boiled vegetables when given occasionally.
• Sinking Pellet Food: There are many sinking pellets or wafers available in the market that are specially made for algae eaters.
• Spirulina-based Food: This contains a lot of protein and essential nutrients, which helps keep them healthy.
• Frozen Food: Occasionally, frozen food like bloodworms or daphnia is also good for them.
Suitable Partners
Some suitable aquatic plants for Siamese Algae Eaters are Java Fern, Anubias, Java Moss, Amazon Sword, and Hornwort, which help improve the aquarium environment in line with their natural behavior.






